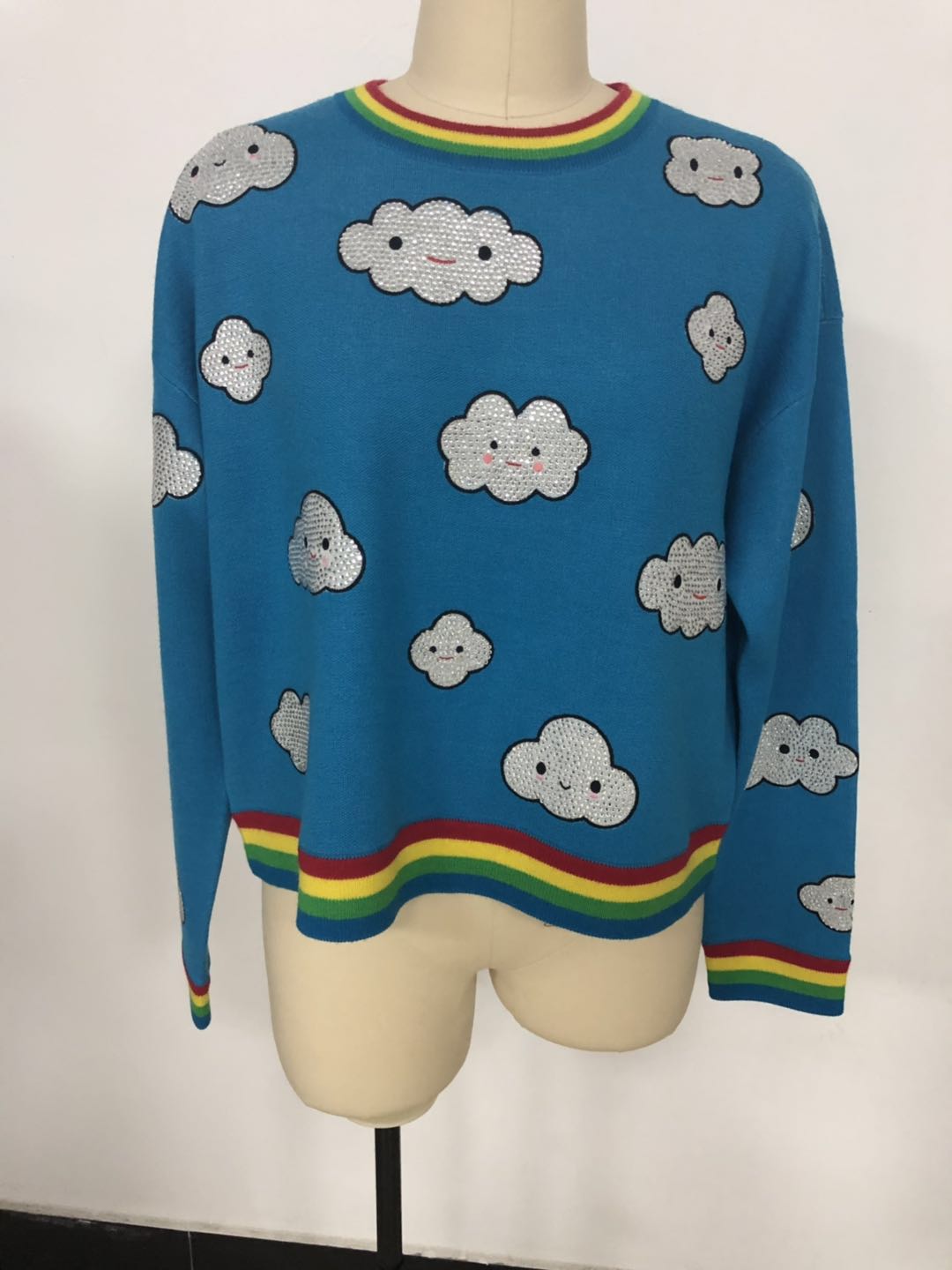
10 Yarns’ Performance Affect the Kinds of Yarns Using
When design a knitwear, we need to consider many elements. For example, which season to wear, fall winter or spring summer? Is it oversize or slim fit? To make fine gauge or heavy gauge? What about the stitches and motifs? And if there is any additional embellishment. Here below lists 10 yarns’ performance affect the kinds of yarn using.
-
Sweater anti-wrinkle. Resistance wrinkle or wrinkle recovery performance during wearing. It is very important when designing the coat styles.
-
Sweater pilling resistance. Pilling occurs due to friction by external force when wearing. Anti-pilling is generally divided into five levels. The fifth level is the best; it means no pilling. The first level is the worst; it means the pilling is the most serious. Among them cashmere and merino wool are easy to pilling.
-
Sweater anti-snagging. It means the fibers and yarns are pulled out of surface due to snagging. It mainly occurs in filament fabrics and knitted sweaters. It not only makes the appearance of the garment not pretty, but also affect the durability of the sweater.
-
Sweater non-ironing property. It means it can keep flat and beautiful, stable shape by no or slight ironing after washing.
-
Sweater shrinkage. Synthetic fiber and blends have the minimum shrinkage. The second is wool and linen. Cotton yarn in the middle which has a little large shrinkage. The biggest are viscose fiber, artificial cotton and acrylic.
-
Sweater drapability. It means sag due to its own weight. It is one of the important contents in visual form style and aesthetic comfort. It relates to whether the sweater can form a beautiful curved shape when used.
-
Sweater gloss. Raw material and thickness of yarn, twist size and yarn density are the factors that affect the gloss of the sweater. For the same material yarn, the gloss of sweater depends on the external structure of the sweater and the dyeing.
-
Sweater warmth retention. On the one hand its characteristics of yarn itself. On the other hand, the change of stitches has different warming effects.
-
Woven hygroscopicity. Yarn with high hygroscopicity will expand after get wet. The diameter increases and the length decreases. Also the shrinkage rate is large. For example, viscose yarn water absorption up to 13% and its synthetic fiber has poor moisture absorption that its shrinkage rate is small. The shrinkage varies with the density of the sweater.
-
Sweater air-permeability. It is the basic performance in sweater permeability which is affect wearing comfort. Such as heat insulation, warmth preservation, permeability and coolness.